Recently, NCU has seen an array of advances in photoacoustic imaging in its Imaging and Visual Representation Laboratory of the School of Information Engineering. Among them, papers on sparse-view reconstruction for photoacoustic tomography and on targeting the narrow depth of field of optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy,completed by the team led by young teacher Song Xianlin of the Department of Electronic and Information Engineering, was published in Photoacoustics, a top journal in photoelectricity, and in Journal of Biophotonics (selected as the cover page) and Journal of Biomedical Optics, top international journals in biomedical photonics respectively.
The first paper, Sparse-view reconstruction for photoacoustic tomography combining diffusion model with model-based iteration, published in the top journal Photoacoustics (Q1 TOP, IF="7.9), was jointly completed by Song Xianlin and Wang Guijun, 2021 master degree candidate in Communication Engineering under the guidance of Professor Liu Qiegen.

As a non-invasive hybrid medical imaging technology, photoacoustic tomography combines the strengths of optical imaging and acoustic imaging. However, the sparse-view reconstruction has been suffering artifacts in photoacoustic tomography. To solve the problem, the paper proposes a novel model-based sparse reconstruction method for photoacoustic tomography via diffusion model. In the training process, by adding noise slowly, the team learns the data distribution and get the continuous-time score function to solve the reverse SDE. During the reconstruction phase, the research takes the sparse-view photoacoustic signal as the input and tries to achieve the iteration solution through the data consistency term between prediction corrector and the data in the model, thus achieving higher-quality reconstruction. The results of the datasets of both the simulated blood vessel and the mice’s abdomen indicate that the method proposed can achieve higher-quality reconstruction for photoacoustic tomography.
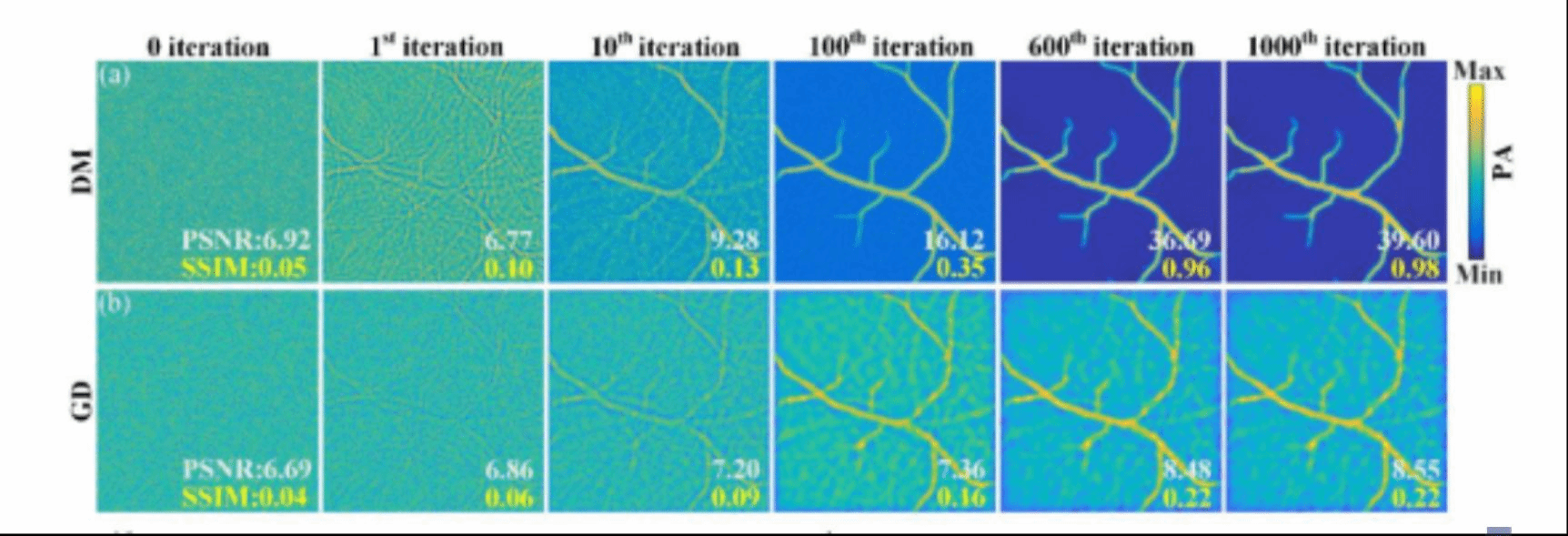
The second paper, Noise-insensitive defocused signal and resolution enhancement for optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy via deep learning, completed by the team led by Song Xianlin, was published on October 6th in Journal of Biophotonics (a top international journal in biomedical optics), appearing on both the cover page and the first page. The paper was jointly completed by teachers and students of NCU, with Song Xianlin and Liu Qiegen as the corresponding authors, undergraduate team members Wang Rui and Zhang Zhipeng as the co-first authors, and Chen Ruiyi and Yu Xiaohai as participants.
Optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy has been facing problems of narrow depth of field and significant degradation in defocused signal intensity and spatial resolution. To address these problems, the paper proposes a deep-learning based method to improve the defocus resolution and signal-to-noise ratio. A virtual photoacoustic microscope based on k-wave is used to obtain the datasets of deep learning under different noise levels and a fully dense U-Net is trained with randomly distributed point sources. The result shows that the PSNR of defocused signal is enhanced by more than 1.2 times. An over 2.6-fold enhancement in lateral resolution and an over 3.4-fold enhancement in axial resolution of defocused regions are achieved. The large volumetric and high-resolution imaging of blood vessels further verifis that the proposed method can effectively overcome the degradation of the signal and the spatial resolution due to the narrow depth of field of optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy. This method provides a low-cost and easy way to achieve wide depth of field, which is expected to be applied to vivo imaging of non-planar biological tissues (such as cerebral vessels and hepatic sinusoid).
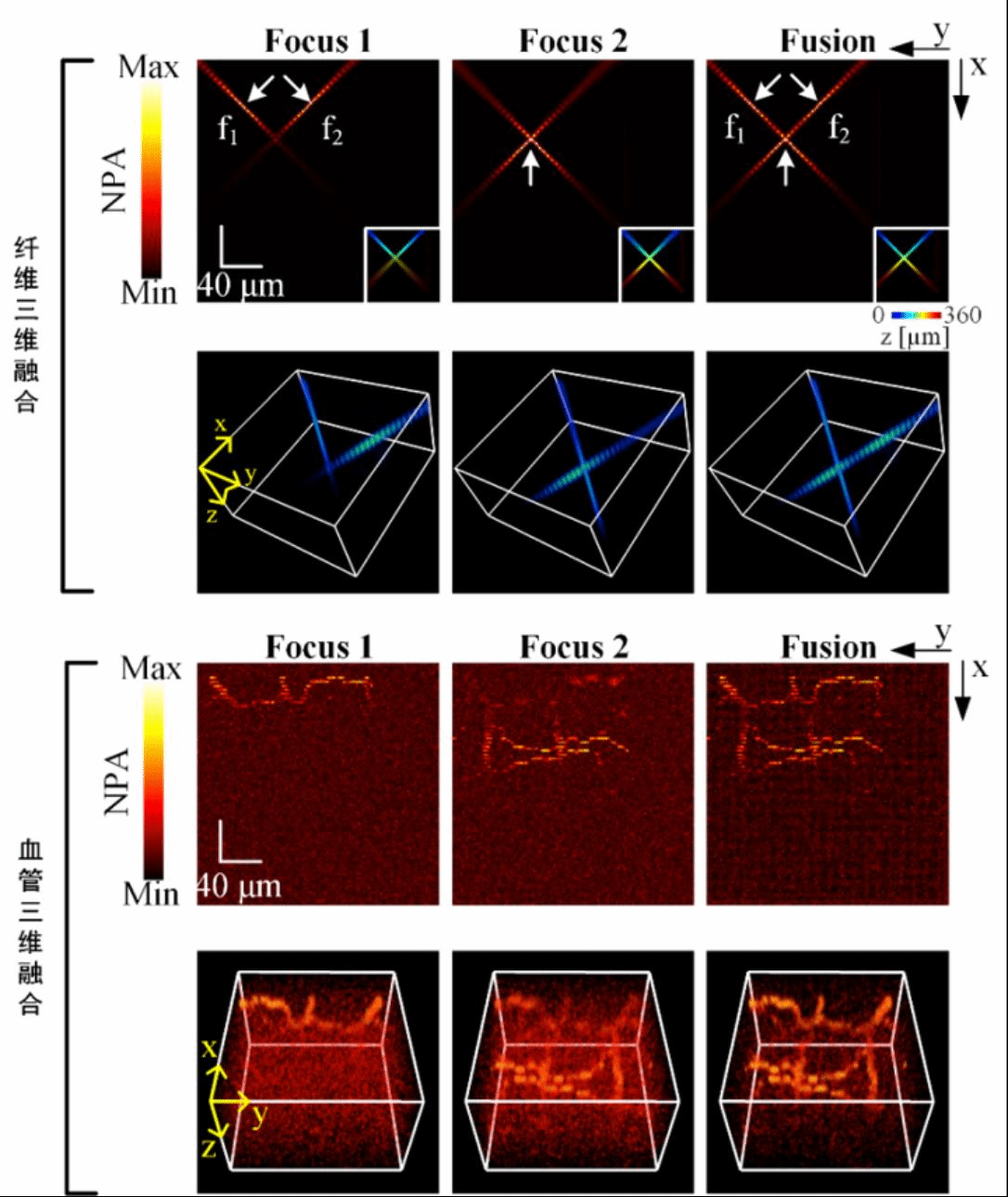
The third paper, Noise insensitive volumetric fusion method for enhanced photoacoustic microscopy, also completed by the team led by Song Xianlin, was published on October 4th in Journal of Biomedical Optics, another top international journal in biomedical optics. The paper was jointly completed by teachers and students of NCU, with Song Xianlin as the corresponding author, undergraduate team members Li Sixing, Wuhao and Zhang Hongyu as the co-first authors, and the undergraduate student Zhang Zhipeng as participants.

In this paper, a cost-effective 3D photoacoustic information fusion method is proposed to facilitate the acquisition of large volumetric and high-resolution photoacoustic image. According to the method, firstly, the focused regions in multi-focus photoacoustic data are identified with the proposed 3D modified Laplacian operator. Then the result is corrected by the majority filter and Gaussian filter (GF). Finally, the acquisition of large volumetric and high-resolution photoacoustic image can be achieved by the voxel-wise weighted-averaging data. The findings suggest that the DoF of photoacoustic microscopy can be expanded by a factor of 1.7 while maintaining the lateral resolution within focused regions through the proposed method. The method is also applicable to the photoacoustic microscopy under different noise levels and to biological samples with intricate structure. Through the proposed method, the volumetric imaging capacity can be further enhanced without changing the hardware structure of the imaging system, thereby helping in the imaging of biological tissues with a rough surface (e.g., cerebrovascular) and in the fast acquisition of physiological and pathological processes in a large scale.
The above-mentioned research is based on the Imaging and Visual Representation Laboratory of NCU, which is affiliated with the Artificial Intelligence Industrial Research Institute of NCU. The Laboratory is led by Professor Liu Qiegen, winner of the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China. Based on the national strategic needs and the economic development of Jiangxi Province, the lab focuses on the development needs of industries such as magnetic resonance and CT imaging, computational optical imaging, VR display. It centers on tackling the bottlenecks of the key technologies and engineering in the process of “sensor imaging - signal processing - enhanced display” and carries out systematic research based on imaging and visual representation. In recent years, the lab has achieved fruitful results in talent training and social services, such as winning the Gold Medal in the China International College Students’ ‘Internet+’ Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition and the First Prize in National College Students’ ‘Artificial Intelligence+’ Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Creation Competition. In 2022, the lab won the Youth Science and Technology Award of the Chinese Society for Stereology, and some of its projects were included in the List of Top Projects of Jiangxi Province and the List of Top Projects of Nanchang City for the First Session.
Web links of the papers
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pacs.2023.100558
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jbio.202300149
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37799936/
Web link of the lab
https://www.labxing.com/lab/1018;https://github.com/yqx7150
Editor: Cheng Huiping
Executive Editor: Tu Jinfeng




